Cashew constituent anacardic acid studied as potential candidate for pancreatic cancer treatment
09/18/2018 / By Edsel Cook
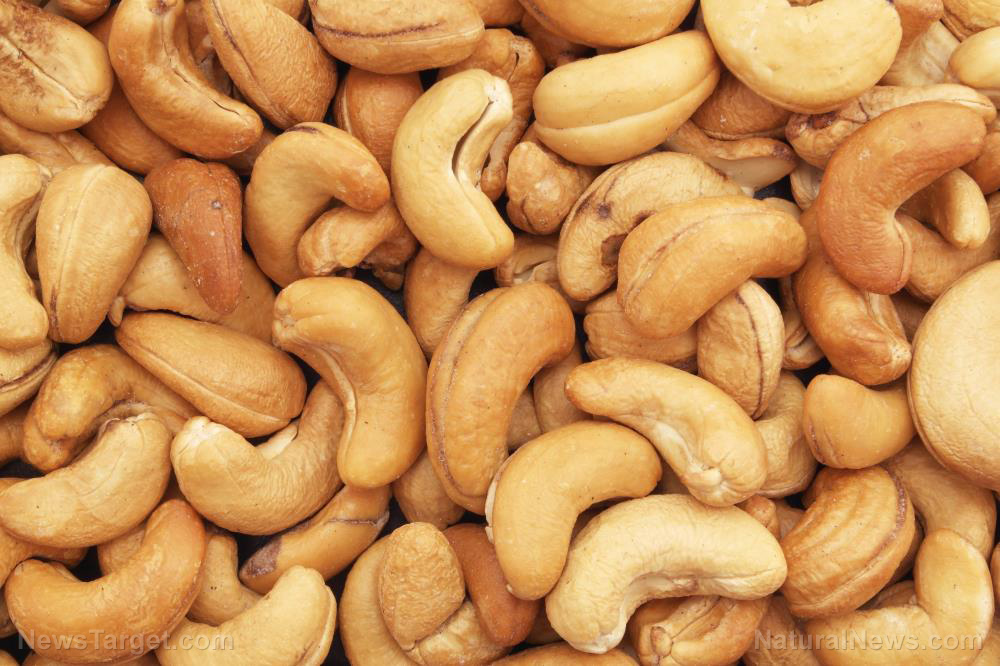

American researchers investigated the possible use of anacardic acid – a natural substance derived from the fruit and seed of the cashew tree – in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. They showed that the phenolic lipid is able to inhibit the growth of pancreatic cancer cells.
The study was supported by the University of Pikeville. The results were published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Cultures of human pancreatic cancer cells were treated with either anacardic acid, a combination of anacardic acid and 5-Fluorouracil, or anacardic acid and Gemcitabine.
- Various tests were performed to determine the cytotoxic effect of the three treatments, the synergy between anacardic acid and its partners, and the signaling molecules used by anacardic acid to achieve any cancer-mitigating activity.
- Anacardic acid demonstrated an anticancer effect that depended on the dosage. It improved the cytotoxic effects of 5-Fluorouracil and Gemcitabine.
- The acid achieved its cancer-fighting effect by activating three signaling molecules: Chromatin Modifying Protein 1A (Chmp1A), Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), and p53. The levels of Chmp1A were increased by the three anticancer substances, which seemed to indicate that this molecule-mediated the cytotoxic effect.
- In silencing tests, anacardic acid was shown to rely on Chmp1A for its anticancer effects. 5-Fluorouracil and Gemcitabine did not need the signaling molecule.
The researchers closed their study with the statement that anacardic acid should be further tested as a complementary supplement for abating the start or development of pancreatic cancer.
You can read the complete paper at this link.
To learn more about natural substances that possess the same anticancer potential as anacardic acid, visit AntiCancer.news.
Journal Reference:
Park M, Upton D, Blackmon M, Dixon V, Craver S, Neal D, Perkins D. ANACARDIC ACID INHIBITS PANCREATIC CANCER CELL GROWTH, AND POTENTIATES CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC EFFECT BY CHMP1A – ATM – P53 SIGNALING PATHWAY. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2018;18(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2139-3
Tagged Under: anacardic acid, anticancer, anticancer compounds, anticancer treatment, cancer, Cashews, cytotoxic, dietary supplements, pancreatic cancer, pancreatic cancer treatment, supplements