CoQ10 helps relieve symptoms of congestive heart failure, prevents premature death in patients
05/17/2020 / By Divina Ramirez
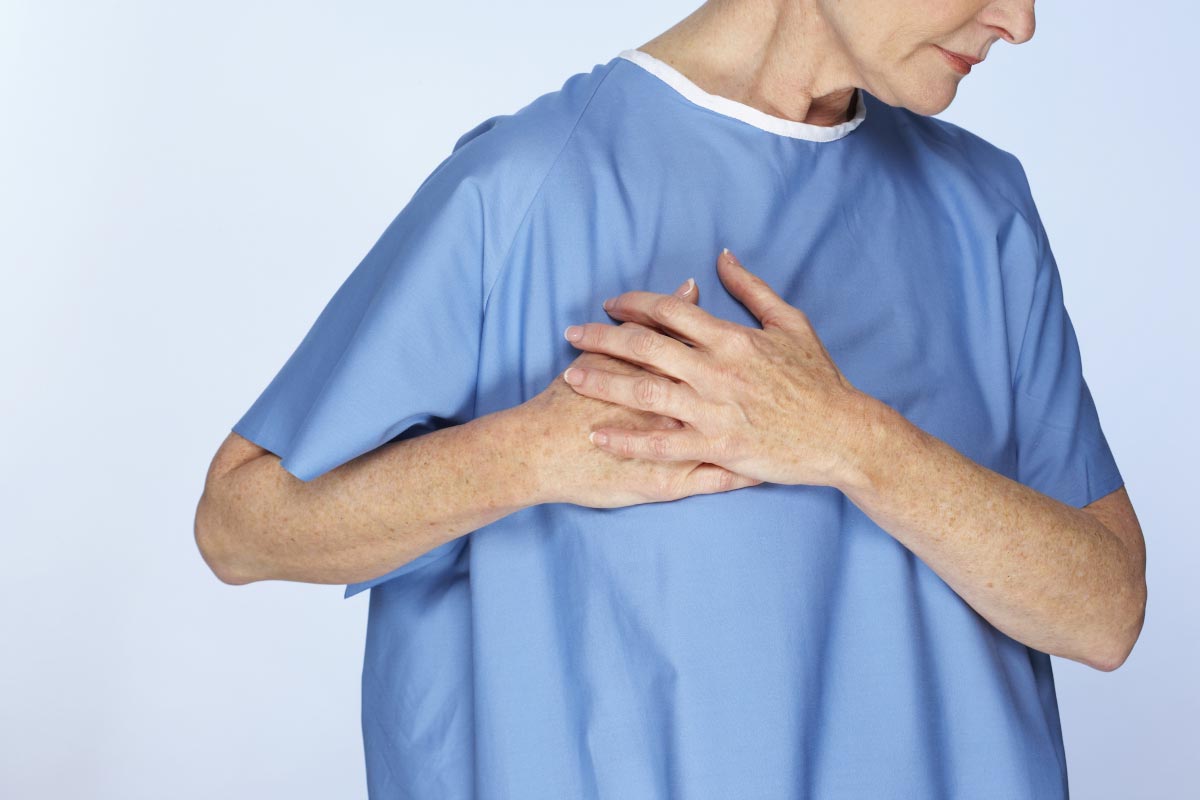
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is one of the most popular dietary supplements in the United States. Extensive studies suggest that the antioxidant properties of CoQ10 can be utilized for the treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
A recent review published in Circulation: Heart Failure found that CoQ10 supplementation can reduce the risk of premature death in patients with heart failure. CoQ10 supplementation also improved overall blood circulation and stimulated the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the heart.
What is coenzyme Q10?
CoQ10 is a fat-soluble chemical found in almost every cell in the body. Its primary function is to help convert food into energy.
CoQ10 is also involved in the production of ATP, an important molecule that powers cellular processes. Without adequate levels of CoQ10, cells will not be able to carry out essential bodily functions like digestion, metabolism and respiration.
CoQ10 also acts as an antioxidant to protect cells from inflammation due to disease-causing free radicals. These are unstable molecules that can cause irreversible damage to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) if left unchecked. Oxidative stress and inflammation due to free radical damage have also been linked to neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
The body produces CoQ10 naturally. But as with most things, this process slows down over time. Because of the importance of CoQ10, low levels of this chemical might have serious implications for health.
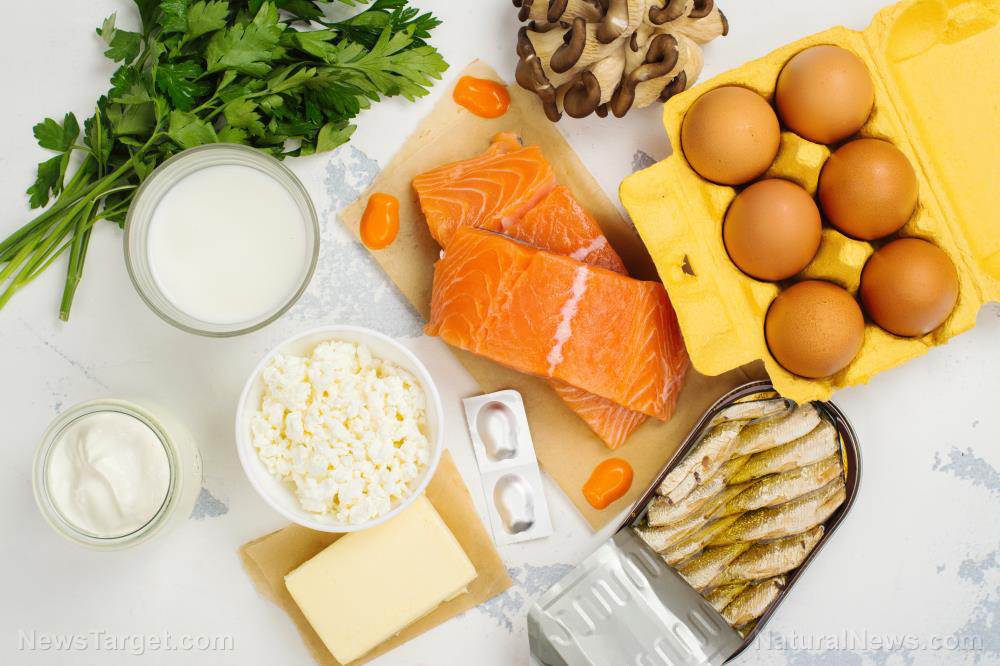
That said, CoQ10 deficiency can be easily prevented, even in later life. Plenty of foods contain CoQ10, including lean meat, animal organs, fatty fishes, healthy oils and citrus fruits. Incorporating these into a balanced diet helps supply the body with CoQ10.
In case of severe deficiency, a healthcare professional might encourage taking CoQ10 supplements.
The effects of CoQ10 on the heart
Recent studies suggest that CoQ10 might be beneficial for people with cardiovascular conditions. A team of researchers from Duke University’s School of Medicine in North Carolina found that CoQ10 supplementation can improve symptoms of congestive heart failure. This chronic condition affects the pumping power of the heart muscles.
In people with congestive heart failure, the heart is unable to keep up with the body’s needs, thus increasing the risk of premature death.
Remarkably, the researchers found that several studies on CoQ10 and heart health reported improved markers of congestive heart failure in people who took 60–300 milligrams (mg) of CoQ10 supplements daily.
In particular, CoQ10 supplementation fortified the heart and blood vessels, thus enhancing blood circulation. The researchers also found evidence that CoQ10 supplementation increased the amount of ATP in the heart. High levels of ATP are crucial for people with congestive heart failure since ATP helps boost the pumping power of the heart muscles.
Based on their findings, the researchers thus concluded that CoQ10 supplementation could be an effective therapeutic option for people with congestive heart failure. (Related: Researchers identify 3 antioxidants that help minimize inflammation in heart failure patients.)
Other supplements for heart health
Besides CoQ10 supplements, several other dietary supplements can help boost heart health. Most of these supplements contain potent antioxidants and active plant compounds that improve markers linked to cardiovascular conditions, including high cholesterol, high blood pressure and arterial stiffness.
These supplements include:
- Multivitamins
- Psyllium fiber
- Omega-3 oils
- Magnesium
- L-Carnitine
- Green tea extract
- Garlic
Supplements for heart health can minimize the risk of cardiovascular conditions. That said, keep in mind that supplements cannot be used as a substitute for proper diet and nutrition. Eating a balanced diet and exercising often are still the most effective ways to prevent chronic diseases.
Learn more about congestive heart failure and other cardiovascular conditions at Heart.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: #nutrition, alternative medicine, biomedical research, cardiovascular health, Coenzyme Q10, disease treatments, future science, heart disease, longevity, nutrients, prevention, supplements
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 NUTRIENTS NEWS