Versatile melatonin: More than just improving sleep, this hormone can protect against Alzheimer’s, reduce anxiety, and more
06/13/2018 / By Zoey Sky
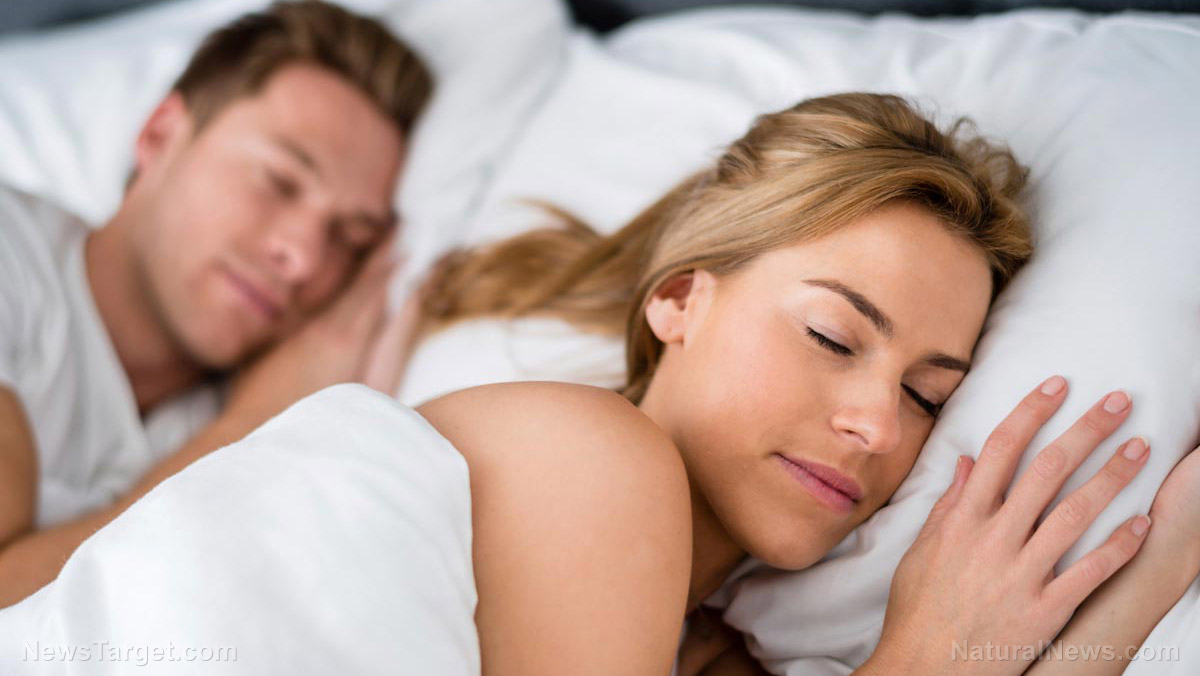

If you’ve had trouble sleeping because of stress or other factors, the natural hormone melatonin can help promote “deep, restful sleep” that is crucial to your physical and emotional well-being.
Aside from its use in treating sleeping disorders, research has proven that the sleep hormone can also minimize anxiety, soothe heartburn, relieve migraines, prevent Alzheimer’s disease, and even improve treatment outcomes for cancer patients.
The many benefits of melatonin
Melatonin is a chemical neurotransmitter synthesized in the body from the amino acid tryptophan. The pineal gland secretes melatonin, and the hormone helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythm (biological clock).
Melatonin also promotes healthy sleep patterns. Aside from inducing sleep, melatonin can also relieve anxiety and promote a stable mood.
In a meta-analysis published in Sleep Medicine Reviews, researchers who examined 15 different sleep studies determined that melatonin greatly reduced the amount of time it took for the participants to fall asleep. The hormone also increased sleep duration.
The results also showed that melatonin can improve the length and quality of daytime sleep. Melatonin supplementation was also proven to help night-shift workers and individuals who have “reverse sleep schedules.” (Related: Skip the night lights, get black out curtains: Everyone, no matter what your age, should sleep in total darkness for the best mental health.)
Since melatonin can control the body’s circadian rhythm, it also functions as an effective remedy for jet lag.
A powerful antioxidant, the hormone can also protect the body from oxidative damage that can cause diseases, as well as neutralize dangerous free radicals. Unlike other antioxidants, melatonin is more efficient since it can easily diffuse into cells and pass through the blood-brain barrier.
A clinical study also showed that compared to Prilosec (omeprazole), melatonin is more effective at relieving heartburn since the hormone is necessary for gastrointestinal functioning. Researchers have discovered that the versatile hormone can protect the esophagus from the side effect of gastric acid, making it a potential therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
In a separate study, 351 participants with moderate-to-severe heartburn were separated into two groups. The first group received six milligrams (mg) of melatonin daily, which was combined with B-complex vitamins and amino acids like methionine and taurine.
The second group received the pharmaceutical medication Prilosec. After a week, the melatonin group reported improvement. Forty days after they received the hormone, their symptoms were completely resolved, unlike the Prilosec group which only had a 66-percent recovery rate.
Meanwhile, data from a year-long study published in the European Journal of Cancer revealed that melatonin can decrease the risk of cancer cell growth. For the study, researchers observed 250 patients undergoing chemotherapy for advanced cancers of the breast, head, gastrointestinal tract, lung, and neck that were divided into two groups.
The first group only received chemotherapy, using drugs like cisplatin and gemcitabine. The second group received 20 mg of melatonin a day along with their medications.
After the study ended, those in the melatonin group had a higher rate of survival and “enhanced regression of tumors.” The second group was also protected against the various side effects of toxic cancer drugs like fatigue, heart damage, lowered platelet count, mouth sores, and neurotoxicity.
Additionally, studies published in the Journal of the Danish Medical Association suggested that supplementation with melatonin can double a cancer patient’s chance of survival. Individuals with various cancers can have an increased survival rate from 28 percent to 52 percent, showing that the hormone has “great potential in treating cancer.”
There are also ongoing studies looking into the possible uses of melatonin when it comes to protecting the brain from neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
However, only a handful of research groups around the world have looked into the potential benefits of melatonin. One reason for the lack of interest could be the fact that melatonin is a natural and easily accessible substance that is hard to patent and provides little to no earning potential for the pharmaceutical industry.
Boosting your melatonin intake
Since levels of beneficial melatonin often decline with age, supplements can boost your melatonin levels. To have a good night’s sleep, integrative physicians recommend dosages of at least 1-3 mg taken about 30 minutes before bedtime.
Take note that exposure to artificial white light, e.g. from cell phones, at night will decrease melatonin levels. Don’t use your cell phone at night so you don’t disrupt your sleep cycle.
To treat heartburn, take about six mg of melatonin daily. For cancer-prevention, studies prescribe at least three to 50 mg a day.
You can also eat more foods rich in tryptophan, which is converted into melatonin. Sources include dairy products (raw milk, cheese), fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds (flax, sesame), and seafood (halibut, shrimp).
You can read more articles about the other benefits of melatonin and other hormones at Healing.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Alzheimer's disease, Anxiety, anxiety relief, cancer, disease prevention, heartburn, hormones, melatonin, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, natural sedative, nutrients, oxidative damage, research, restful sleep, reverse sleep schedules, sleep, sleep problems, supplements, tryptophan